Why Postman Fails to Send Requests and How to Fix It: A Complete Guide
Postman is one of the most popular ways to test APIs. It is an important part of the development and quality assurance tools because it has a simple design, lots of strong features, and support for many protocols. But Postman can sometimes not work the way you want it to, just like any other tool.
What is one of the most annoying problems? What happens when I click "Send"? There was no answer, no mistake, just quiet, or even worse, a message that wasn't clear about how to fix the problem. This problem can quickly get in the way of your work, whether you're trying a local API or talking to a third-party website.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the most common reasons why Postman fails to send requests, along with practical solutions to troubleshoot and fix each one. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced user, these tips will help you get your API testing back on track quickly.
1. Check Your Internet Connection
The first thing to rule out is your network. Postman needs a working internet connection to communicate with external APIs. If you're sending requests to online services (not local environments), even a short outage can cause failures.
What to do:
- Open a browser and try loading a website.
- Restart your modem or switch networks.
- If on a company network, make sure the firewall isn't blocking Postman.
If your internet is down or restricted, Postman will be unable to reach external servers.
2. Verify the API Endpoint URL
Even a small typo in the URL can cause Postman to silently fail or return vague errors.
Things to check:
- Make sure the base URL is correct (e.g., https://api.example.com/v1/endpoint)
- Confirm that the domain and path exist.
- If you're using variables (like {{baseUrl}}), ensure they're defined in your environment.
Also, double-check the protocol—using http instead of https (or vice versa) can cause blocked requests, especially with strict CORS policies or server configurations.
3. Disable SSL Certificate Verification (For Local APIs)
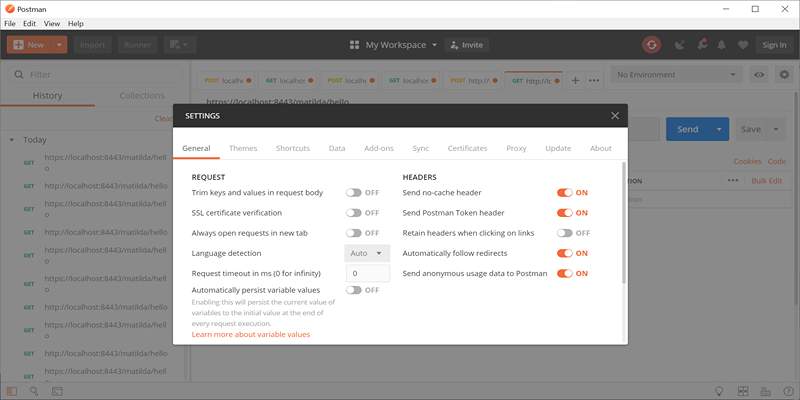
When testing APIs hosted on localhost or development environments with self-signed certificates, Postman may block the request due to SSL errors.
Solution:
- Go to Settings (top right corner gear icon).
- Under the General tab, toggle off SSL certificate verification.
- Restart the request.
This allows Postman to proceed without validating the certificate—perfect for local or staging APIs that aren't publicly signed.
4. Confirm Server Availability
Your API server may not be running or might be experiencing downtime.
Check:
- If you're testing a local server (like Node.js or Flask), ensure it's started and listening.
- Use the terminal or browser to hit the same URL. If the server doesn't respond there either, it's not Postman's fault.
If it's a third-party API, check their status page or try sending the same request from a browser to confirm it's working.
5. Look for Proxy Interference
Some proxy servers can block requests sent from Postman, especially if the proxy settings are misconfigured.
To fix:
- Open Postman Settings > Proxy.
- If you're not using a proxy, turn Global Proxy Configuration off.
- If you're behind a corporate proxy, make sure credentials are correctly configured.
Also, try disabling test again to see if the issue resolves.
6. Use Postman Console to Inspect the Request
The Postman Console is your best friend when something breaks. It gives you a detailed view of each request sent, including headers, payload, and errors.
To open it:
- Click View > Show Postman Console or press Ctrl + Alt + C.
This will display what's happening behind the scenes when you click "Send." Look for:
- Failed network calls
- Misconfigured headers
- Timeout errors
- Environment variable problems
7. Check for Authorization Errors
Some APIs require an authentication token, API key, or OAuth credentials. If you try to access protected endpoints without the correct auth setup, the request may fail silently or return a 401 error.
What to do:
- Go to the Authorization tab in Postman.
- Make sure you're using the correct type (e.g., Bearer Token, Basic Auth, API Key).
- Confirm the token or credentials are current and not expired.
Also, double-check the header values—typos here can cause authentication to fail even if the format looks right.
8. Review Timeout Settings
By default, Postman waits for 30 seconds for a response. If your API takes longer than that, the request will fail due to a timeout.
To increase timeout:
- Open Settings > General.
- Scroll down to Request timeout in ms.
- Increase the value (e.g., set to 60000 for 60 seconds).
This is particularly helpful for slow or heavily loaded servers during testing.
9. Inspect Request Body and Headers
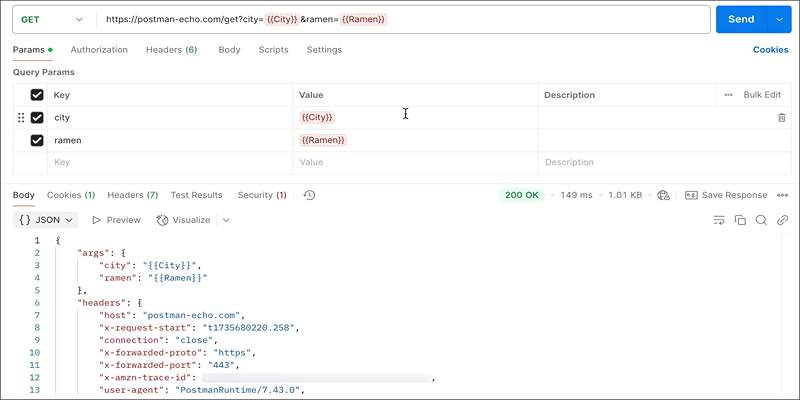
A malformed request body or missing content-type header can cause the server to reject the request without a proper response.
Tips:
- If sending JSON, make sure:
- The Body tab is set to "raw"
- The content-type is application/json
- The JSON is properly formatted
- For form submissions, use "x-www-form-urlencoded" or "form-data" as appropriate.
Don't forget to validate your JSON before sending—use a linter or JSON validator to be sure.
10. Restart Postman or Your System
Sometimes, the issue is simply Postman itself. It might have cached something incorrectly or encountered a temporary glitch.
Fix:
- Close and reopen Postman.
- If that doesn't work, restart your computer.
- If the problem continues, uninstall and reinstall Postman (make sure to back up your collections).
A fresh restart often resolves background issues that don't show up in the UI.
Conclusion
When Postman fails to send requests, it can feel like you're working in the dark. But with a structured approach—checking your URL, inspecting headers, using the Postman Console, and reviewing system settings—you can usually identify and resolve the issue quickly.
Most of the time, the problem lies in network settings, endpoint configurations, or authorization errors. By going through the steps outlined in this guide, you'll not only fix the immediate issue but also sharpen your debugging skills for future projects.
Don't let a stubborn request block your workflow. With the right tools and knowledge, you'll have Postman back in action in no time.
On this page
1. Check Your Internet Connection What to do: 2. Verify the API Endpoint URL Things to check: 3. Disable SSL Certificate Verification (For Local APIs) Solution: 4. Confirm Server Availability Check: 5. Look for Proxy Interference To fix: 6. Use Postman Console to Inspect the Request To open it: 7. Check for Authorization Errors What to do: 8. Review Timeout Settings To increase timeout: 9. Inspect Request Body and Headers Tips: 10. Restart Postman or Your System Fix: ConclusionRelated Articles

Top 7 UI/UX Design Tools Every Designer Should Know

Programmatic SEO: How Can You Increase Search Traffic Using No-Code Tools

Which Are The 7 Best URL Shorteners: Simplify Your Links in 2025

Top Bug Tracking Tools to Streamline Your Workflow

5 Free PDF to Word Converters That Leave No Watermarks Behind

Make Gmail Searches Smarter: Optimizing Google Workspace for Speed

Troubleshooting GitHub Push Errors Related to Authentication

How to Declutter Your Digital Workspace: A Complete Guide to Boost Productivity
Perplexity vs. ChatGPT

Which Free Converter Keeps Image Quality: PNG to JPG or PNG to WEBP?

How to Use Free Tools Online to Convert EPUB Files to PDF Format

 knacksnews
knacksnews